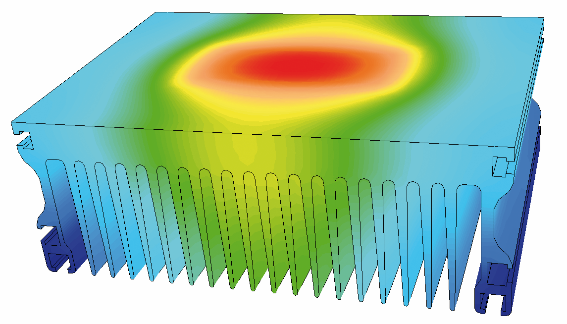
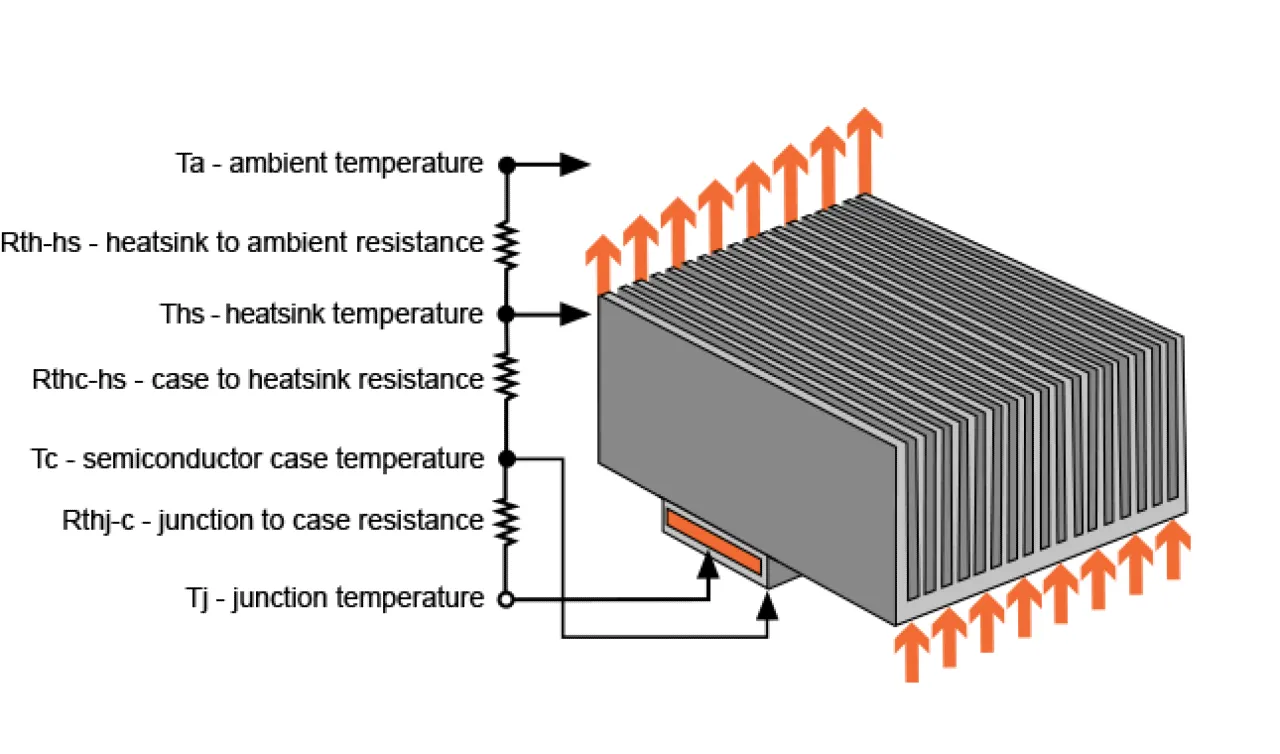
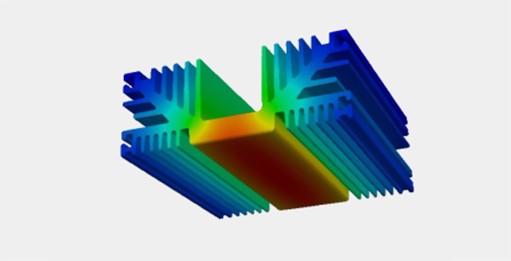
A heatsink is a device that is used to dissipate heat from electronic components, such as processors and power transistors. The primary function of a heatsink is to remove the heat generated by these components and transfer it to the surrounding air, thus keeping the temperature of the electronic components within a safe operating range.
One of the main reasons why we need heatsinks is because electronic components generate a significant amount of heat during operation. This heat can cause the components to malfunction or fail, leading to costly repairs or replacements. By dissipating the heat, a heatsink can help to prolong the lifespan of electronic components and ensure that they operate at their maximum efficiency.
Another reason why heatsinks are important is because they can help to reduce the overall temperature inside an electronic device, such as a computer. This can help to prevent overheating, which can lead to system crashes, data loss, and other problems.
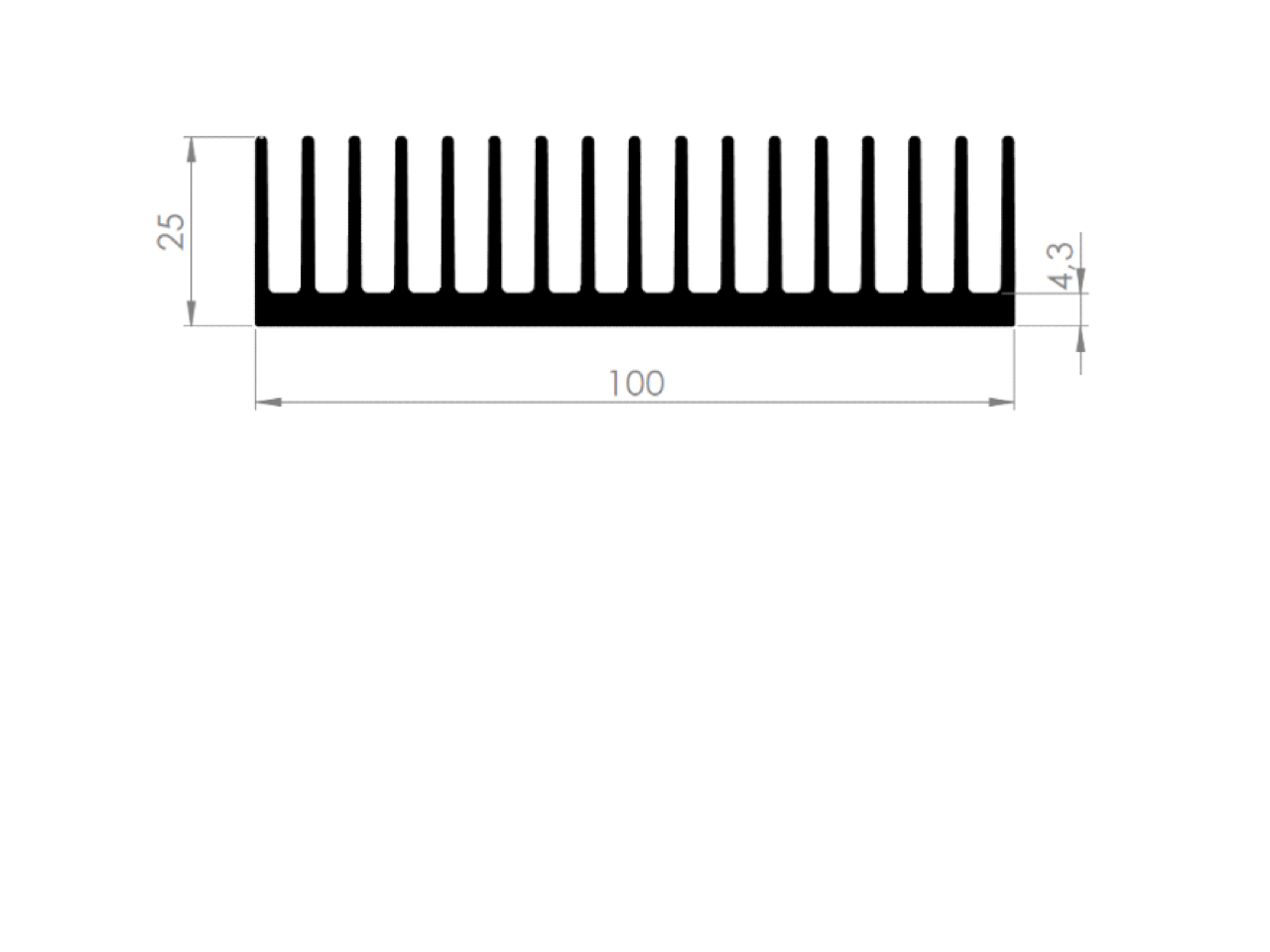
Heatsinks come in a variety of shapes and sizes and can be made from different materials, such as aluminum, copper, and even heat-conductive plastics. The most common type of heatsink is the "fins" type, which is made of aluminum or copper and has a series of fins that increase the surface area for heat dissipation.
In summary, a heatsink is a device that is used to dissipate heat from electronic components, thus keeping the temperature of the electronic components within a safe operating range, prolonging the lifespan of electronic components, and reducing the overall temperature inside an electronic device.